Publications
2025
-
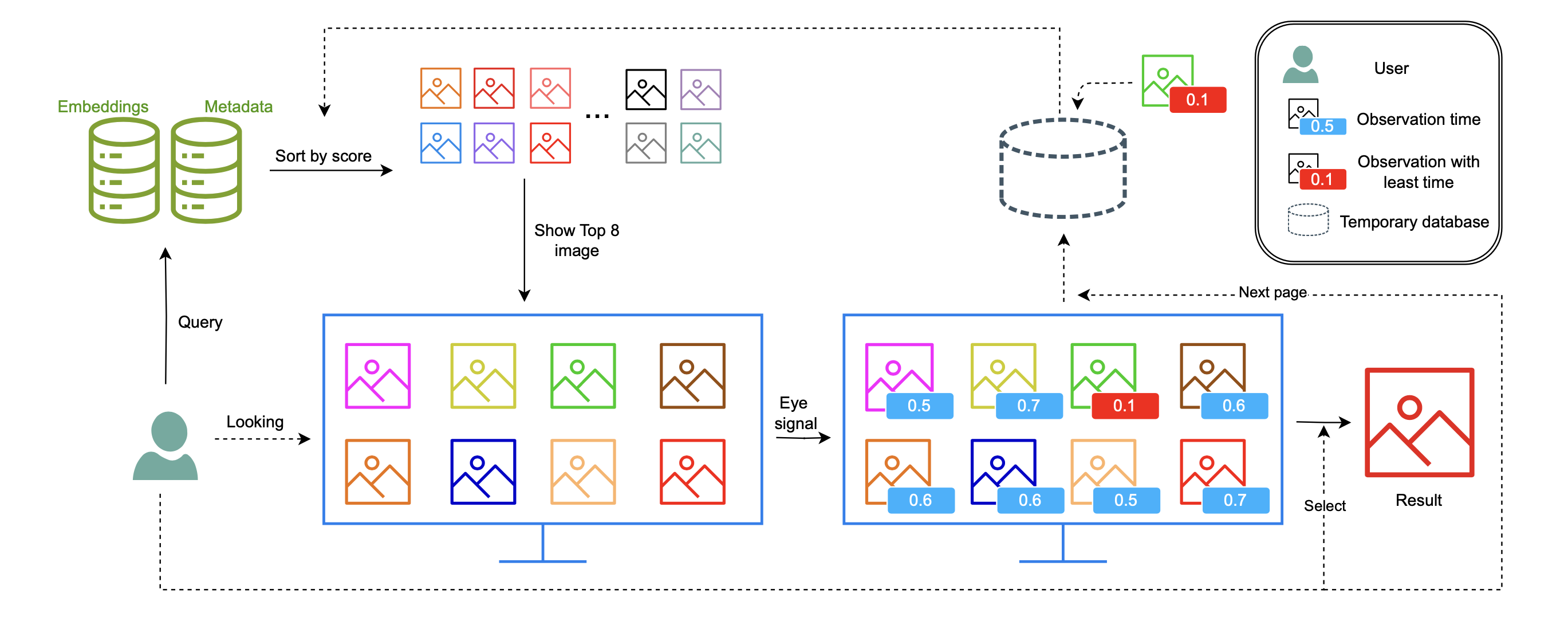 VEAGLE: Eye Gaze-Assisted Guidance for Video Browser ShowdownThang-Long Nguyen Ho , Viet-Tham Huynh, Onanong Kongmeesub , and 4 more authorsIn International Conference on Multimedia Modeling , 2025
VEAGLE: Eye Gaze-Assisted Guidance for Video Browser ShowdownThang-Long Nguyen Ho , Viet-Tham Huynh, Onanong Kongmeesub , and 4 more authorsIn International Conference on Multimedia Modeling , 2025In this work, we focus on assisting users in finding information that may have been unintentionally overlooked. Our system supports not only experienced users but also newcomers to Video Browser Showdown systems, enabling them to search for information more quickly and accurately. During the querying process, users might unintentionally miss important images, including those they are specifically looking for. By leveraging eye-tracking technology, our system records the user’s gaze duration on each image. The system will highlight images that match the user’s search descriptions but were viewed for only a short period, and suggest these images again to the user. By tracking eye movements, our system provides a comfortable user experience while also enhancing search capabilities, promising further development potential in the future.
@inproceedings{long2025VEAGLE, title = {VEAGLE: Eye Gaze-Assisted Guidance for Video Browser Showdown}, author = {Nguyen Ho, Thang-Long and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Kongmeesub, Onanong and Tran, Minh-Triet and Dongyun, Nie and Graham, Healy and Cathal, Gurrin}, booktitle = {International Conference on Multimedia Modeling}, year = {2025}, organization = {Springer}, } -
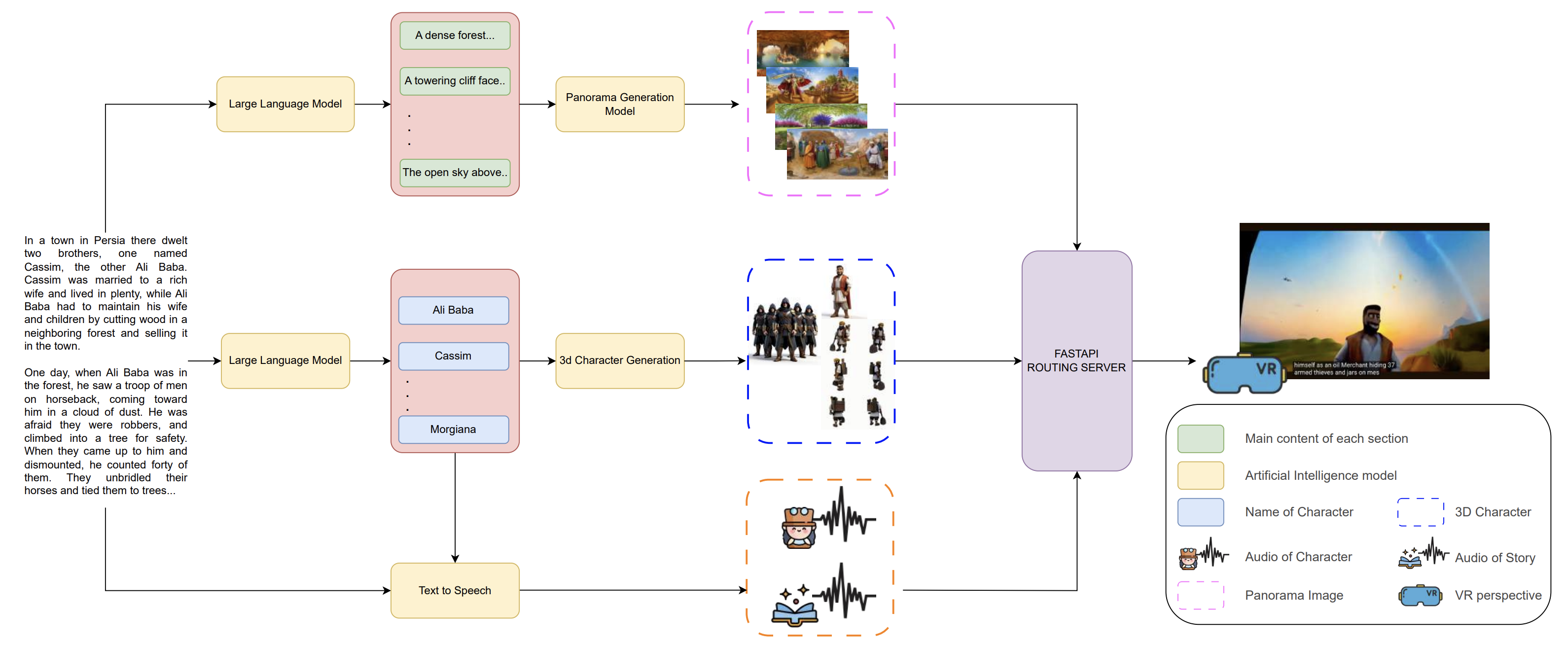 From Story to Reality: Generative VR for Immersive Fairy TalesCong-Triet Huynh , Nhut-Thanh Le-Hinh , Minh Triet Tran , and 1 more authorIn The 9th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Virtual & Augmented Reality Simulations , 2025
From Story to Reality: Generative VR for Immersive Fairy TalesCong-Triet Huynh , Nhut-Thanh Le-Hinh , Minh Triet Tran , and 1 more authorIn The 9th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Virtual & Augmented Reality Simulations , 2025Fairy tales have served as vital cultural narratives for centuries, cultivating imagination and moral reasoning through symbolic storytelling. However, traditional consumption methods, such as static text, illustrations, and basic animations, fundamentally limit user engagement by restricting spatial understanding and imaginative immersion. While VR offers revolutionary potential, its development is costly, time-consuming, and technically complex. Generative AI offers solutions by automating resource-intensive content creation. Our AI system combines: (1) diffusion models for 360° images, (2) transformer-based 3D model synthesis, and (3) neural voice generation. This integrated pipeline improves production efficiency and personalization. At the same time, its multi-modal generation across visual, auditory, and narrative domains suggests a scalable approach for immersive storytelling that preserves cultural authenticity via generative AI. The review results indicate that most participants favored the VR version over the eBook format. Specifically, the average rating for the Story Experience criterion among 31 participants was 4.4 for the VR version, compared to 4.0 for the eBook version.
@inproceedings{triet2025ICVARS, title = {From Story to Reality: Generative VR for Immersive Fairy Tales}, author = {Huynh, Cong-Triet and Le-Hinh, Nhut-Thanh and Tran, Minh Triet and Huynh, Viet-Tham}, booktitle = {The 9th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Virtual & Augmented Reality Simulations}, year = {2025}, } -
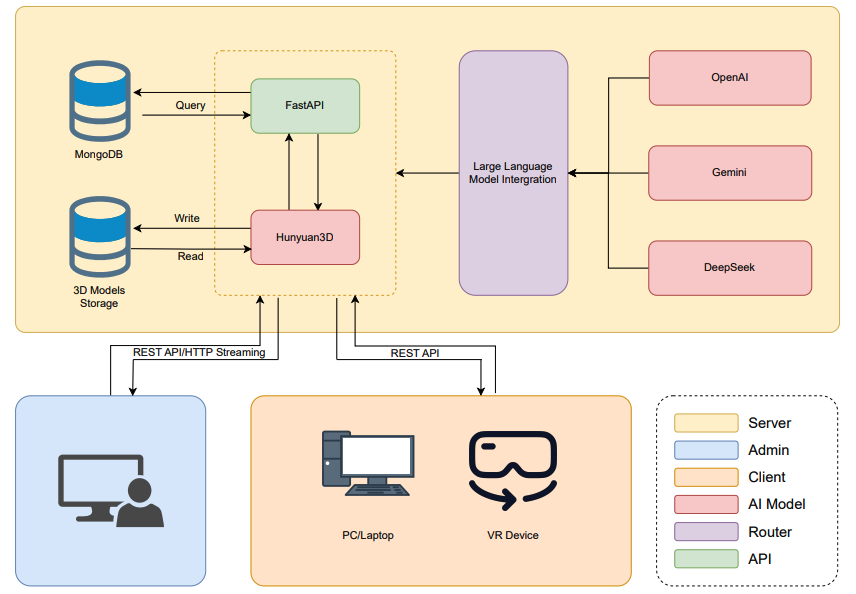 EcoLearn: AI-Powered Escape Room Simulations for Teaching Children Waste Classification and Problem-SolvingNhut-Thanh Le-Hinh , Cong-Triet Huynh , Minh Triet Tran , and 1 more authorIn The 9th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality , 2025
EcoLearn: AI-Powered Escape Room Simulations for Teaching Children Waste Classification and Problem-SolvingNhut-Thanh Le-Hinh , Cong-Triet Huynh , Minh Triet Tran , and 1 more authorIn The 9th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality , 2025Children represent a rapidly evolving generation that is increasingly exposed to diverse technological advancements. A key challenge is ensuring their interaction with these technologies occurs naturally and beneficially. Moreover, as technological development accelerates, there is a growing tendency among younger individuals to overlook fundamental life skills, including waste classification. We proposed EcoLearn, an educational system designed to enhance children’s reasoning abilities while promoting effective waste classification in a dynamic, non-scripted environment to address this issue. EcoLearn incorporates parental and classifier supervision, where parents and relatives contribute by generating waste items for classification. The system is an Escape Room simulation that challenges users to complete tasks to escape, integrating interactive games, detailed instructions, Large Language Models, and 3D Generative AI to enhance user engagement. Based on the evaluation of 11 users who tested both the Personal Computer and Virtual Reality versions, the results indicate that users tended to prefer the VR version of the application, with the VR version scoring an average of 3.92 compared to the PC version’s average score of 2.92. By fostering an interest in reasoning and environmental responsibility, EcoLearn serves as an initial step toward harnessing AI-driven virtual reality gaming without predefined scenarios.
@inproceedings{thanh2025AIVR, title = {EcoLearn: AI-Powered Escape Room Simulations for Teaching Children Waste Classification and Problem-Solving}, author = {Le-Hinh, Nhut-Thanh and Huynh, Cong-Triet and Tran, Minh Triet and Huynh, Viet-Tham}, booktitle = {The 9th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality}, year = {2025}, } -
 Towards safer roads: benchmarking object detection models in complex weather scenariosBa-Thinh Tran-Le , Patel Vatsa , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 4 more authorsMachine Vision and Applications, 2025
Towards safer roads: benchmarking object detection models in complex weather scenariosBa-Thinh Tran-Le , Patel Vatsa , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 4 more authorsMachine Vision and Applications, 2025The performance of object detection models in adverse weather conditions remains a critical challenge for intelligent transportation systems. Since advancements in autonomous driving rely heavily on extensive datasets, which help autonomous driving systems be reliable in complex driving environments, this study provides a comprehensive dataset under diverse weather scenarios like rain, haze, nighttime, or sun flares and systematically evaluates the robustness of state-of-the-art deep learning-based object detection frameworks. Our Adverse Driving Conditions Dataset features eight single weather effects and four challenging mixed weather effects, with a curated collection of 50,000 traffic images for each weather effect. State-of-the-art object detection models are evaluated using standard metrics, including precision, recall, and IoU. Our findings reveal significant performance degradation under adverse conditions compared to clear weather, highlighting common issues such as misclassification and false positives. For example, scenarios like haze combined with rain cause frequent detection failures, highlighting the limitations of current algorithms. Through comprehensive performance analysis, we provide critical insights into model vulnerabilities and propose directions for developing weather-resilient object detection systems. This work contributes to advancing robust computer vision technologies for safer and more reliable transportation in unpredictable real-world environments.
@article{thinh2025mva, title = {Towards safer roads: benchmarking object detection models in complex weather scenarios}, author = {Tran-Le, Ba-Thinh and Vatsa, Patel and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Tran, Mai-Khiem and Kunal, Agrawal and Tran, Minh-Triet and Nguyen, Tam V.}, journal = {Machine Vision and Applications}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Springer}, } -
 LUMINA-1: Learning and Understanding Multimedia in Immersive Navigable Archives for Lifelog RetrievalNhut-Thanh Le-Hinh , Cong-Triet Huynh , Minh-Quan Ho-Le , and 3 more authors2025
LUMINA-1: Learning and Understanding Multimedia in Immersive Navigable Archives for Lifelog RetrievalNhut-Thanh Le-Hinh , Cong-Triet Huynh , Minh-Quan Ho-Le , and 3 more authors2025As immersive technologies like Virtual Reality and the Metaverse advance, they open up new possibilities for interactive engagement with multimedia content across various domains, including education, cultural heritage, and creative design. In this paper, we introduce LUMINA-1, a VR-based multimedia lifelog retrieval system designed to support intuitive and immersive exploration of personal visual archives. LUMINA-1 offers a seated virtual workspace that enables users to interact naturally using Gaze Interaction, Hand Gestures, and Context-Aware Controls, eliminating the need for physical locomotion. The system combines efficient feature extraction with real-time visual feedback to deliver responsive query handling and a seamless user experience in immersive environments. These features have contributed to establishing Lumina-1 as one of the pioneering VR-based lifelog information retrieval systems, enabling users to perform queries more naturally and efficiently. This advancement lays the groundwork for the next generation of VR information retrieval systems.
@article{lumina1, title = {LUMINA-1: Learning and Understanding Multimedia in Immersive Navigable Archives for Lifelog Retrieval}, author = {Le-Hinh, Nhut-Thanh and Huynh, Cong-Triet and Ho-Le, Minh-Quan and Ho, Duy-Khang and Tran, Minh-Triet and Huynh, Viet-Tham}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 8th Annual ACM Workshop on the Lifelog Search Challenge}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery}, } -
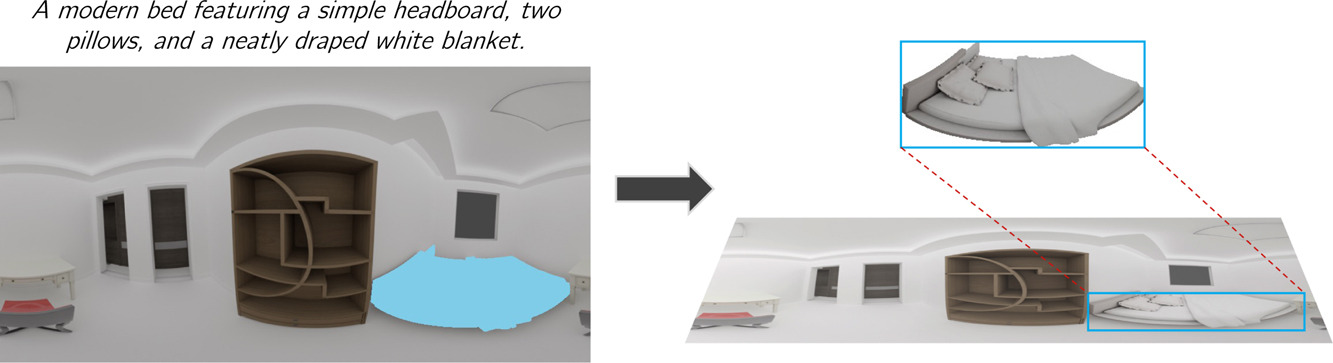 SHREC 2025: Retrieval of Optimal Objects for Multi-modal Enhanced Language and Spatial Assistance (ROOMELSA)Trong-Thuan Nguyen , Viet-Tham Huynh, Quang-Thuc Nguyen , and 30 more authorsComputers & Graphics, 2025
SHREC 2025: Retrieval of Optimal Objects for Multi-modal Enhanced Language and Spatial Assistance (ROOMELSA)Trong-Thuan Nguyen , Viet-Tham Huynh, Quang-Thuc Nguyen , and 30 more authorsComputers & Graphics, 2025Recent 3D retrieval systems are typically designed for simple, controlled scenarios, such as identifying an object from a cropped image or a brief description. However, real-world scenarios are more complex, often requiring the recognition of an object in a cluttered scene based on a vague, free-form description. To this end, we present ROOMELSA, a new benchmark designed to evaluate a model’s ability to interpret natural language. Specifically, ROOMELSA attends to a specific region within a panoramic room image and accurately retrieves the corresponding 3D model from a large database. In addition, our ROOMELSA dataset includes over 1,600 apartment scenes, nearly 5,200 rooms, and more than 44,000 targeted queries. Empirically, while coarse object retrieval is largely solved, only one top-performing model consistently ranked the correct match first across nearly all test cases. Notably, a lightweight CLIP-based model also performed well, although it struggled with subtle variations in materials, part structures, and contextual cues, resulting in occasional errors. Notably, these findings highlight the importance of tightly integrating visual and language understanding. By bridging the gap between scene-level grounding and fine-grained 3D retrieval, ROOMELSA establishes a new benchmark for advancing robust, real-world 3D recognition systems.
@article{shrec2025, title = {SHREC 2025: Retrieval of Optimal Objects for Multi-modal Enhanced Language and Spatial Assistance (ROOMELSA)}, author = {Nguyen, Trong-Thuan and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Nguyen, Quang-Thuc and Nguyen, Hoang-Phuc and Le Bao, Long and Minh, Thai Hoang and Nguyen Anh, Minh and Nguyen Tien, Thang and Nguyen Thuan, Phat and Nguyen Phong, Huy and Huynh Thai, Bao and Nguyen, Vinh-Tiep and Nguyen, Duc-Vu and Pham, Phu-Hoa and Le-Hoang, Minh-Huy and Le, Nguyen-Khang and Nguyen, Minh-Chinh and Ho, Minh-Quan and Tran, Ngoc-Long and Le-Hoang, Hien-Long and Tran, Man-Khoi and Tran, Anh-Duong and Nguyen, Kim and Nguyen, Quan Hung and Phan Thanh, Dat and Tran Van, Hoang and Huynh Viet, Tien and Nguyen Viet Thien, Nhan and Vo, Dinh-Khoi and Nguyen, Van-Loc and Le, Trung-Nghia and Nguyen, Tam V. and Tran, Minh-Triet}, journal = {Computers & Graphics}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Elsevier}, }
2024
-
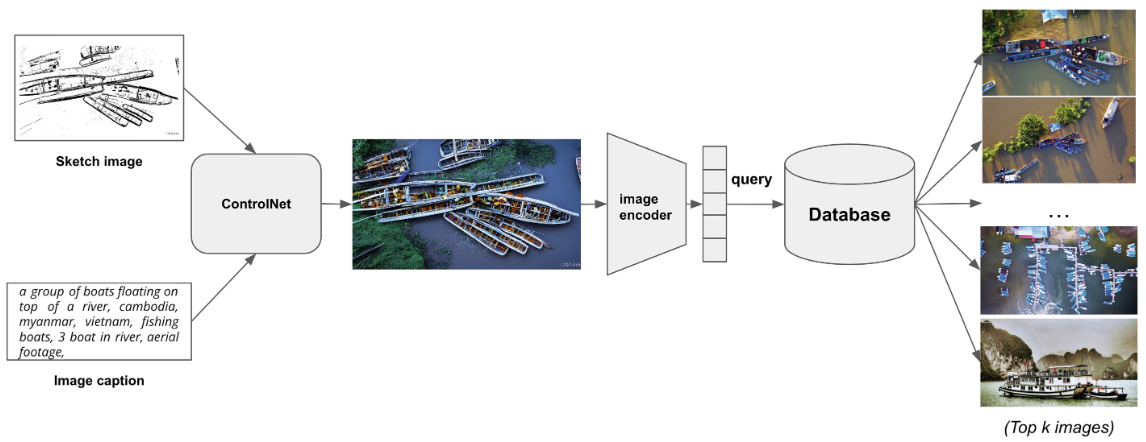 LUMOS-DM: Landscape-Based Multimodal Scene Retrieval Enhanced by Diffusion ModelViet-Tham Huynh, Trong-Thuan Nguyen , Quang-Thuc Nguyen , and 3 more authorsIn International Conference on Multimedia Modeling , 2024
LUMOS-DM: Landscape-Based Multimodal Scene Retrieval Enhanced by Diffusion ModelViet-Tham Huynh, Trong-Thuan Nguyen , Quang-Thuc Nguyen , and 3 more authorsIn International Conference on Multimedia Modeling , 2024Information retrieval is vital in our daily lives, with applications ranging from job searches to academic research. In today’s data-driven world, efficient and accurate retrieval systems are crucial. Our research focuses on video data, using a system called LUMOS-DM: Landscape-based Multimodal Scene Retrieval Enhanced by Diffusion Model. This system leverages Vision Transformer and Diffusion Models, taking user-generated sketch images and text queries as input to generate images for video retrieval. Initial testing on a dataset of 100 h of global landscape videos achieved an 18.78% at Top-20 accuracy rate and 36.45% at Top-100 accuracy rate. Additionally, video retrieval has various applications, including generating data for advertising and marketing. We use a multi-modal approach, combining sketch and text descriptions to enhance video content retrieval, catering to a wide range of user needs.
@inproceedings{huynh2024lumos, title = {LUMOS-DM: Landscape-Based Multimodal Scene Retrieval Enhanced by Diffusion Model}, author = {Huynh, Viet-Tham and Nguyen, Trong-Thuan and Nguyen, Quang-Thuc and Tran, Mai-Khiem and Nguyen, Tam V and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {International Conference on Multimedia Modeling}, pages = {145--158}, year = {2024}, organization = {Springer}, } -
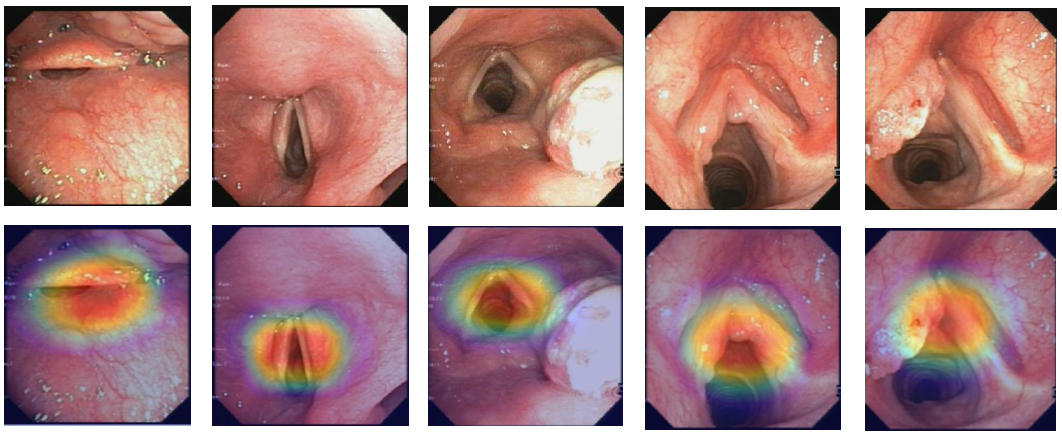 Artificial Intelligence for Laryngoscopy in Vocal Fold Diseases: A Review of Dataset, Technology, and EthicsThao Thi Phuong Dao , Tan-Cong Nguyen , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 3 more authorsMachine Learning, 2024
Artificial Intelligence for Laryngoscopy in Vocal Fold Diseases: A Review of Dataset, Technology, and EthicsThao Thi Phuong Dao , Tan-Cong Nguyen , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 3 more authorsMachine Learning, 2024Laryngoscopy plays a crucial role in providing essential visual access to the larynx, especially vocal folds, for diagnosis and treatment interventions. The field of laryngoscopy is witnessing remarkable advancements driven by artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning, particularly in diagnosing vocal fold disorders. This paper delves into a comprehensive analysis of diverse publicly available laryngoscopy image datasets and cutting-edge deep learning techniques, demonstrating their immense potential to revolutionize diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. However, the ethical and legal challenges surrounding AI in healthcare cannot be overlooked. We meticulously examine critical considerations such as dataset collection, algorithm bias, and responsible clinical application. By addressing these concerns, we emphasize the pivotal role AI can play while ensuring fairness, trust, and adherence to medical ethics. Our aim is to foster a comprehensive understanding of both the potential and the ethical considerations for implementing AI in laryngoscopy. This responsible approach will ultimately lead to improved patient outcomes and a stronger foundation for medical ethics in the age of AI.
@article{thao2024AI, title = {Artificial Intelligence for Laryngoscopy in Vocal Fold Diseases: A Review of Dataset, Technology, and Ethics}, author = {Dao, Thao Thi Phuong and Nguyen, Tan-Cong and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Bui, Xuan-Hai and Le, Trung-Nghia and Tran, Minh-Triet}, journal = {Machine Learning}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Springer}, } -
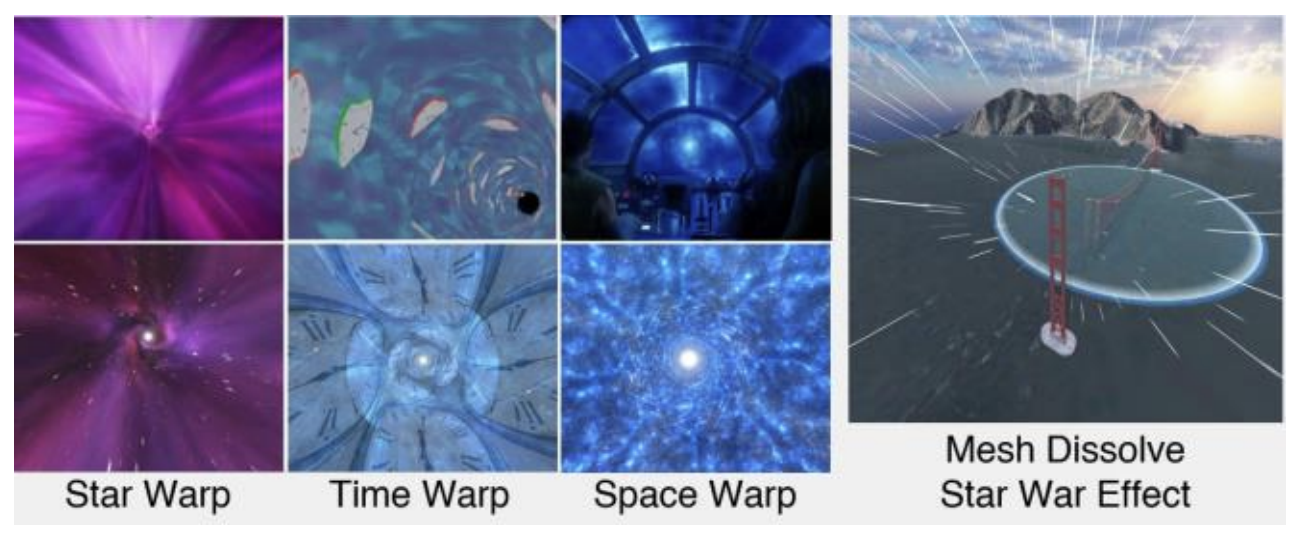 Immersive Spatiotemporal Travel in Virtual RealityThanh Ngoc-Dat Tran , Viet-Tham Huynh, Poojitha Moganti , and 3 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) , 2024
Immersive Spatiotemporal Travel in Virtual RealityThanh Ngoc-Dat Tran , Viet-Tham Huynh, Poojitha Moganti , and 3 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) , 2024Space and Time travel, once confined to science fiction, are now subjects of practical scientific inquiry. However, the practical feasibility of such journeys remains uncertain. This paper aims to investigate and elucidate the effects encountered during simulated space warp and time travel. Specifically, it examines three effects associated with spatial displacement and two effects related to temporal shift, contextualized within the construction phases of five monumental world wonders. Our study, which assesses participants’ perceptions while experiencing these effects through virtual reality headsets, provides valuable insight into the potential of immersive space-time travel simulations and could inspire future developments in the field.
@inproceedings{thanh2024Immersive, title = {Immersive Spatiotemporal Travel in Virtual Reality}, author = {Tran, Thanh Ngoc-Dat and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Moganti, Poojitha and Le, Trung-Nghia and Tran, Minh-Triet and Nguyen, Tam V}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct)}, year = {2024}, organization = {IEEE}, } -
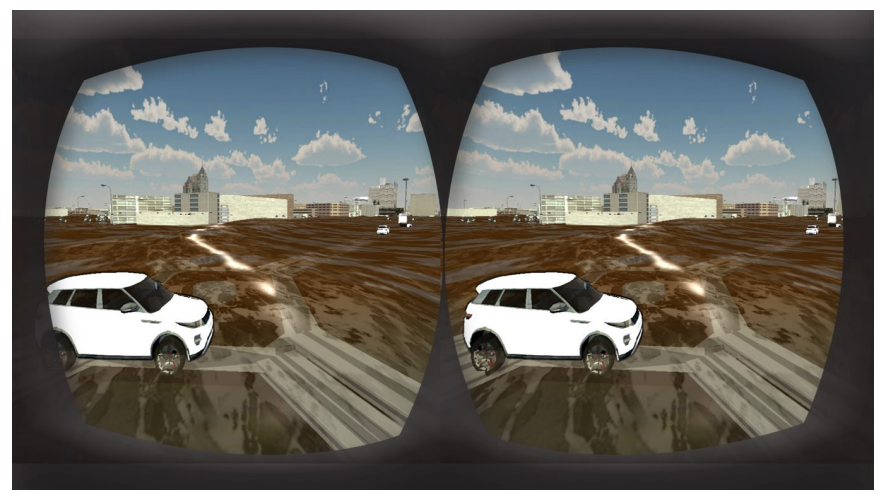 Urban Traffic Planning Simulation with Time and Weather DynamicsTam V. Nguyen , Thanh Ngoc-Dat Tran , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 5 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) , 2024
Urban Traffic Planning Simulation with Time and Weather DynamicsTam V. Nguyen , Thanh Ngoc-Dat Tran , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 5 more authorsIn 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) , 2024Urban traffic planning ensures the efficient design and management of traffic systems, reducing congestion, and improving the safety. Applying virtual reality for urban traffic planning helps city planners visualize and interact with complex traffic systems in a realistic, immersive environment, and improve the decision making process. In this paper, we investigate the integration of the time and weather dynamics into the immersive urban planning system. In particular, we implement the lighting mechanism for rendering the urban simulation scenes in both daytime and nighttime sessions. In addition, we integrate the weather dynamics into the simulator to improve the realism. The user study demonstrates the realism and the engagement of our proposed system.
@inproceedings{tam2024Urban, title = {Urban Traffic Planning Simulation with Time and Weather Dynamics}, author = {Nguyen, Tam V. and Tran, Thanh Ngoc-Dat and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Vatsa, S Patel and Jain, Umang and Tran, Mai-Khiem and Le, Trung-Nghia and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct)}, year = {2024}, organization = {IEEE}, } -
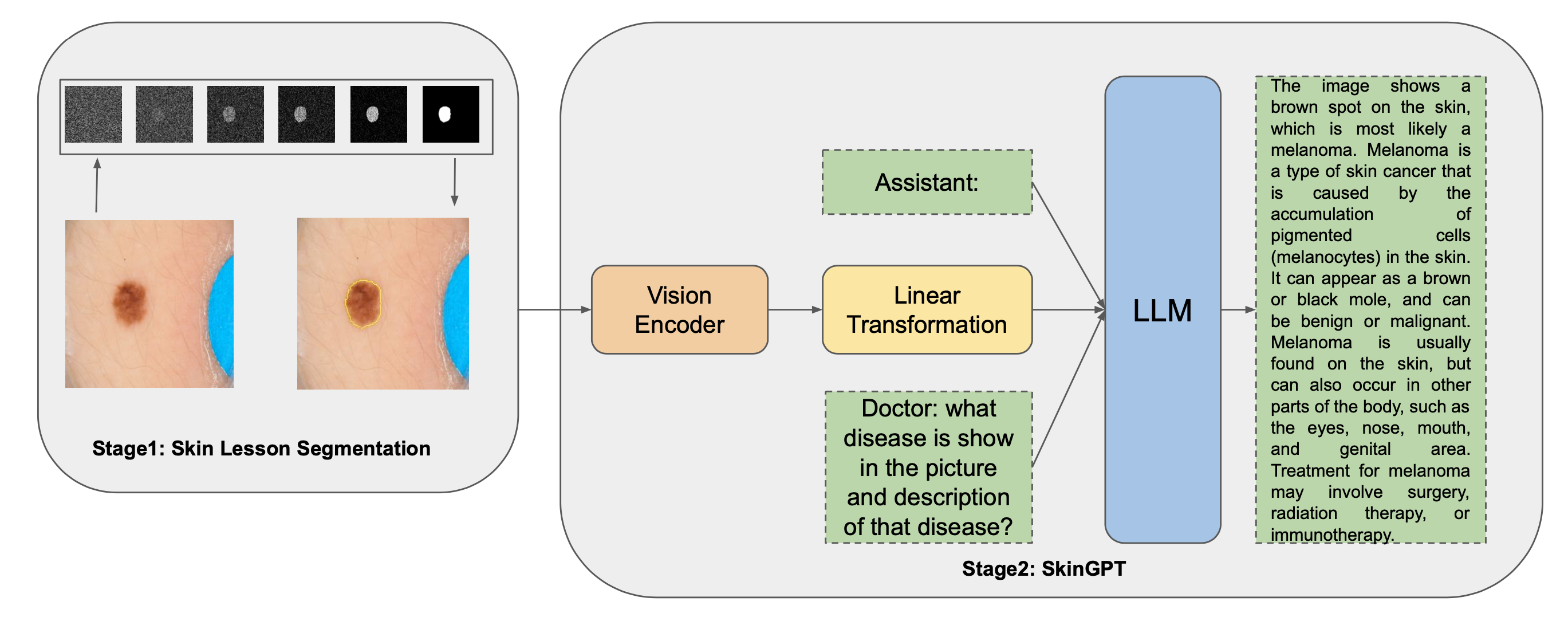 DermAI: A Chatbot Assistant for Skin Lesion Diagnosis Using Vision and Large Language ModelsViet-Tham Huynh*, Trong-Thuan Nguyen* , Thao Thi Phuong Dao , and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) Workshops , 2024
DermAI: A Chatbot Assistant for Skin Lesion Diagnosis Using Vision and Large Language ModelsViet-Tham Huynh*, Trong-Thuan Nguyen* , Thao Thi Phuong Dao , and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) Workshops , 2024In dermatology, the demand for accurate skin lesion diagnoses is critical, especially during peak times like summer when skin cancer screenings surge. The need for efficient processing of large volumes of medical images and the risk of human error highlights the importance of innovative diagnostic tools. This paper introduces DermAI, an advanced AI-driven framework to improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency in skin lesion analysis. DermAI combines a state-of-the-art segmentation model and a large language model to assist clinicians in interpreting medical images swiftly and precisely. Our framework isolates and analyzes key lesion features using advanced segmentation models and vision encoders, while a GPT-4-based language model provides contextual insights to better understand lesion characteristics and potential malignancies. By integrating visual and linguistic analysis, DermAI reduces diagnostic errors, alleviates clinician workloads, and enhances patient care with faster, more accurate results, supporting dermatologists in making informed decisions and advancing AI-assisted diagnostics.
@inproceedings{tham2024DermAI, title = {DermAI: A Chatbot Assistant for Skin Lesion Diagnosis Using Vision and Large Language Models}, author = {Huynh*, Viet-Tham and Nguyen*, Trong-Thuan and Dao, Thao Thi Phuong and Tran, Minh-Triet and Nguyen, Tam V.}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) Workshops}, year = {2024}, organization = {Springer}, } -
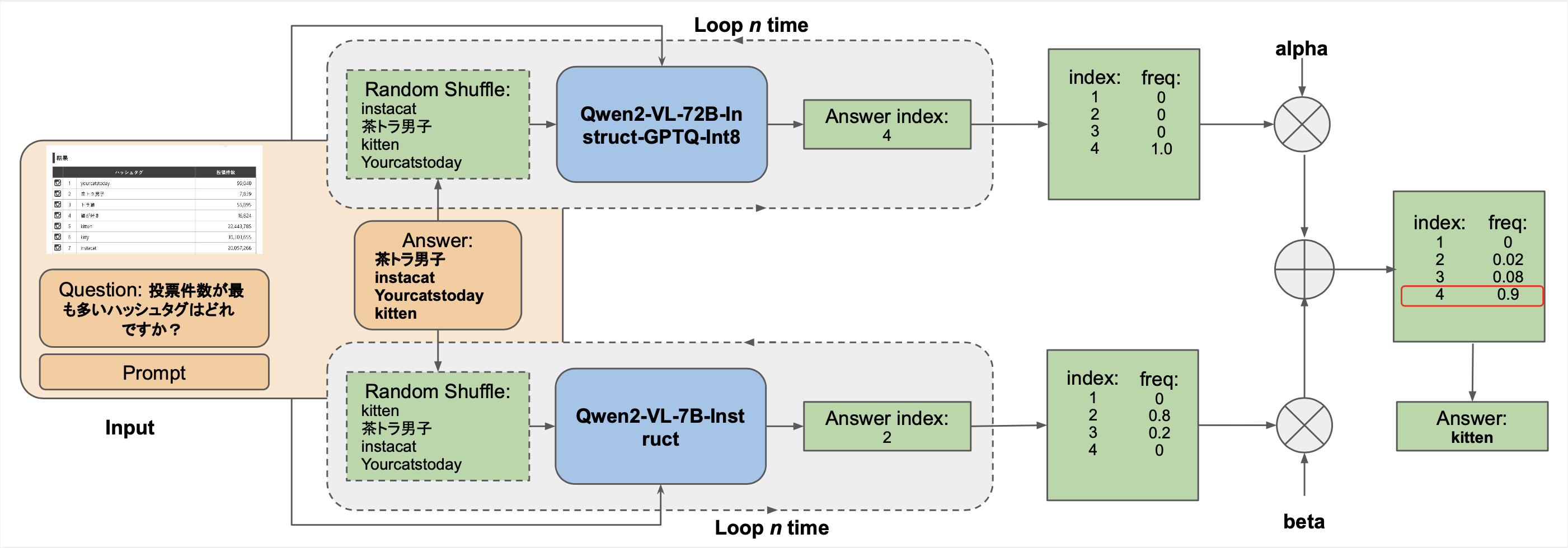 An Approach to Complex Visual Data Interpretation with Vision-Language ModelsThanh-Son Nguyen* , Viet-Tham Huynh*, Van-Loc Nguyen , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) Workshops , 2024
An Approach to Complex Visual Data Interpretation with Vision-Language ModelsThanh-Son Nguyen* , Viet-Tham Huynh*, Van-Loc Nguyen , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) Workshops , 2024The LAVA Workshop 2024 challenge aimed to assess the capability of Large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to accurately interpret and understand complex visual data. This includes intricate visual formats such as data flow diagrams, class diagrams, Gantt charts, and architectural blueprints. In response to this challenge, our research focuses on adapting the MMMU (Multimodal Multitask Understanding) benchmarks to better align with the requirements of visual data interpretation. We propose a comprehensive approach that leverages advanced prompt engineering techniques and incorporates a voting-based ensemble method for aggregating model predictions. This method improves the model’s ability to generalize across different types of visual inputs. Our approach was rigorously evaluated within the context of the challenge, resulting in a total score of 0.85, which ultimately secured the top position in the competition. This result demonstrates the effectiveness of combining prompt engineering with simple yet powerful ensemble strategies for enhancing the performance of VLMs on complex multimodal tasks.
@inproceedings{son2024anapproach, title = {An Approach to Complex Visual Data Interpretation with Vision-Language Models}, author = {Nguyen*, Thanh-Son and Huynh*, Viet-Tham and Nguyen, Van-Loc and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) Workshops}, year = {2024}, organization = {Springer}, pages = {334-350}, } -
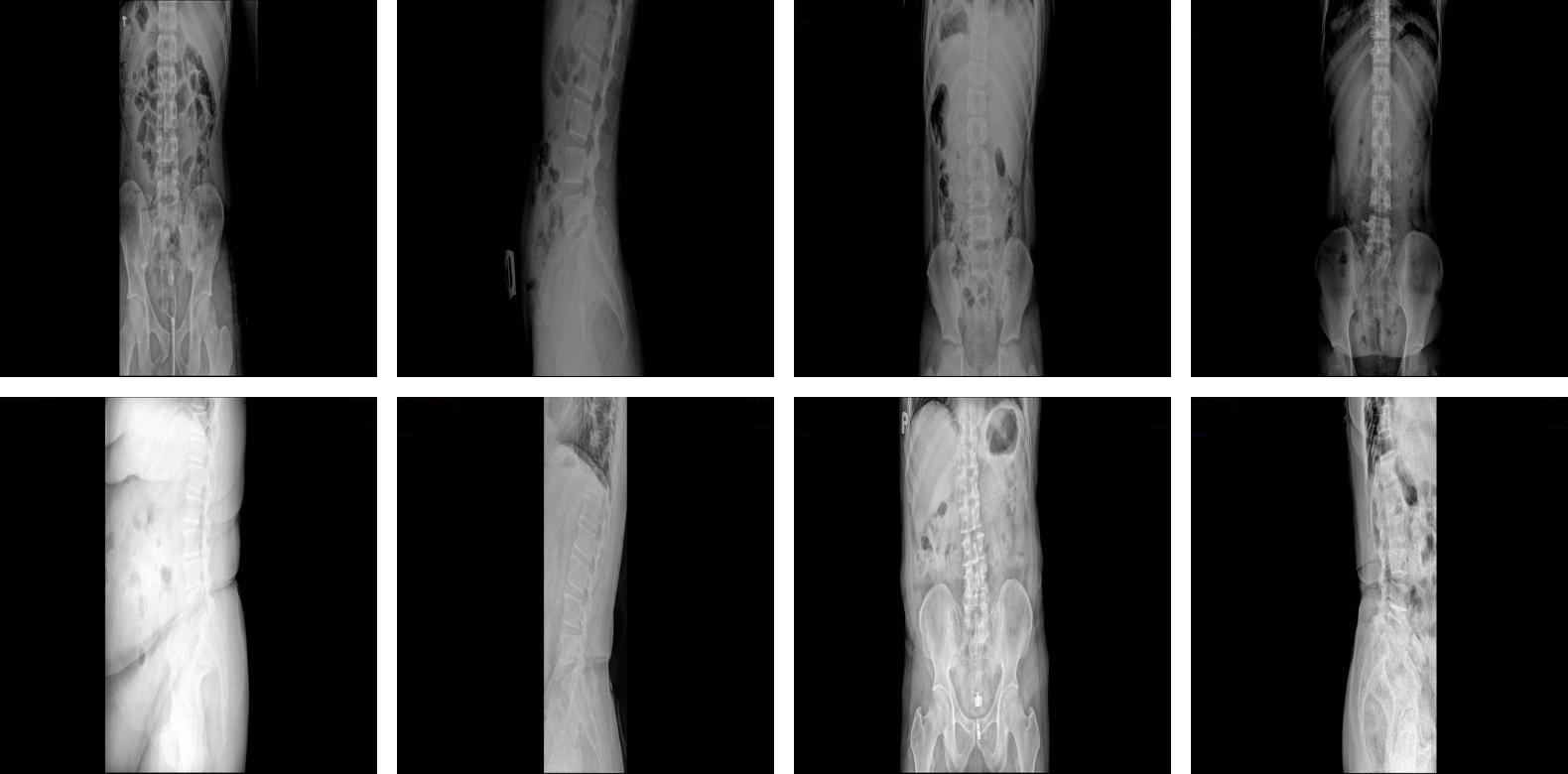 Knowledge Distillation for Lumbar Spine X-ray ClassificationMinh-Khang Nguyen , Viet-Tham Huynh, Thi Thuy-Giang Vo , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2024
Knowledge Distillation for Lumbar Spine X-ray ClassificationMinh-Khang Nguyen , Viet-Tham Huynh, Thi Thuy-Giang Vo , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2024Lumbar spondylosis is a prevalent chronic illness that results in deformation of the lumbar spine and limits human movement. Over time, spinal deformities can compress or exert tension on the nerve roots, resulting in lower back discomfort and disc herniation. The incidence of spondylosis is escalating, attributed to a growing population of younger individuals. This tendency results from alterations like contemporary jobs and education. X-ray imaging of the lumbar spine is widely utilized and endorsed by several physicians for its rapidity, precision, and accessibility across diverse patient populations. This article introduces a technique for detecting and classifying both abnormal and healthy lumbar spine X-ray pictures. After image filtration, we implement Knowledge Distillation, wherein a trained teacher model instructs smaller student models. We employ EfficientNet-B4 as the Teacher model, a high-accuracy and efficient Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture for medical image analysis, and MobileNetV2 as the Student model, which also utilizes the knowledge distillation approach. To assess the model’s performance, 2,000 lumbar spine X-ray pictures were obtained from Kien Giang General Hospital and Trung Cang General Clinic, with 872 samples designated for training and testing. The outcomes attained an accuracy of 91.0%, a precision of 90.0%, a recall of 91.8%, and an F1-score of 90.9%. The findings were achieved after 500 training epochs with a learning rate 0.001. This indicates that our suggested model has strong performance with excellent dependability.
@inproceedings{khang2024KD, title = {Knowledge Distillation for Lumbar Spine X-ray Classification}, author = {Nguyen, Minh-Khang and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Vo, Thi Thuy-Giang and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology}, year = {2024}, organization = {Springer}, } -
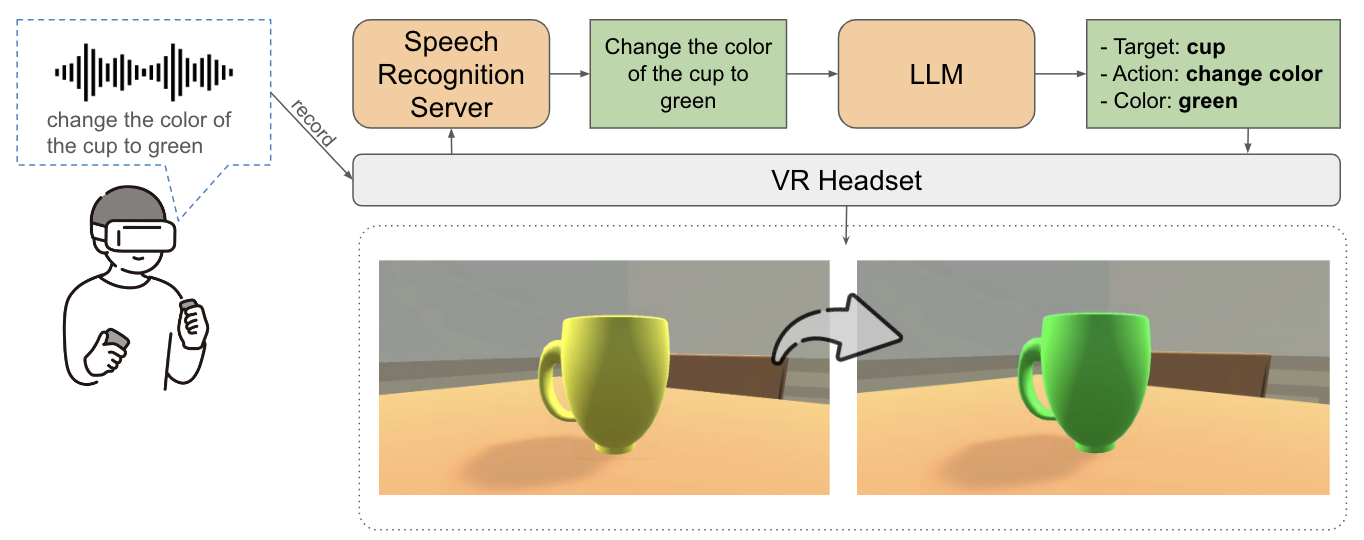 VOI-VR:Voice-driven Object Interaction in Virtual Reality with Large Language ModelsViet-Tham Huynh, Duy-Nam Ly , Hoang-Phuc Nguyen , and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2024
VOI-VR:Voice-driven Object Interaction in Virtual Reality with Large Language ModelsViet-Tham Huynh, Duy-Nam Ly , Hoang-Phuc Nguyen , and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2024This study explores the integration of voice interaction in virtual reality environments to enhance user engagement and accessibility. Utilizing the virtual reality headset, users can interact with 3D objects, such as selecting a cup hidden behind a flower vase, through voice commands instead of traditional controllers, which can be cumbersome in occluded scenarios. Leveraging advancements in large language models (LLMs), we enhance the processing of user voice input for more intuitive interactions. To evaluate effectiveness, we conducted a user study comparing object search and arrangement using controllers versus voice commands in a VR object-finding game. Results indicate that voice interaction significantly improves object identification speed and overall user satisfaction, demonstrating the potential for more immersive VR experiences through innovative interaction modalities.
@inproceedings{tham2024VOIVR, title = {VOI-VR:Voice-driven Object Interaction in Virtual Reality with Large Language Models}, author = {Huynh, Viet-Tham and Ly, Duy-Nam and Nguyen, Hoang-Phuc and Nguyen, Trong-Thuan and Nguyen, Tam V. and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology}, year = {2024}, organization = {Springer}, } -
 Event retrieval from large video collection in Ho Chi Minh City AI challenge 2024Trong-Le Do , Viet-Tham Huynh, Thuc Nguyen-Quang , and 10 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2024
Event retrieval from large video collection in Ho Chi Minh City AI challenge 2024Trong-Le Do , Viet-Tham Huynh, Thuc Nguyen-Quang , and 10 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2024Ho Chi Minh City AI Challenge 2024, now in its fifth edition, focused on advancing event retrieval techniques from large video collections, driving research and innovation in video analysis. The challenge featured a dataset of 1,471 videos spanning 328 h alongside diverse query formats to evaluate system performance in realistic scenarios. Participant teams competed in multiple rounds, addressing complex queries involving temporal and semantic event understanding. Leveraging advanced deep learning models, temporal segmentation, and multimodal fusion techniques, participants showcased innovative approaches across textual and visual Known-Item Search and Question Answering tasks. Visual KIS recorded the highest performance, highlighting the advantages of rich visual context over text-based queries. This paper provides an overview of the challenge organization, dataset, methodologies, evaluation metrics, and insights into trends and solutions observed during the competition.
@inproceedings{le2024soict, title = {Event retrieval from large video collection in Ho Chi Minh City AI challenge 2024}, author = {Do, Trong-Le and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Nguyen-Quang, Thuc and Nguyen, Hai-Dang and Tran, Mai-Khiem and Ninh, Tu V and Le, Tu-Khiem and Ngo, Thanh Duc and Dang-Nguyen, Duc-Tien and Ngo, Tu-Trinh and Schöffmann, Klaus and Gurrin, Cathal and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology}, year = {2024}, organization = {Springer}, }
2023
-
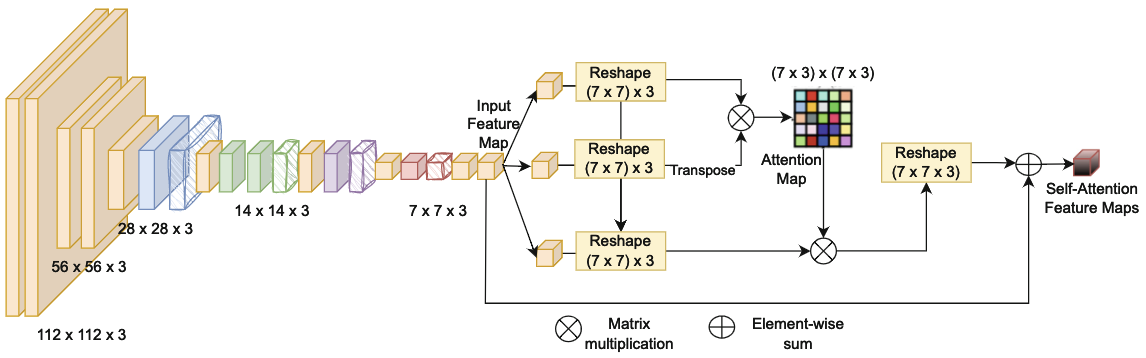 MobileNet-SA: Lightweight CNN with Self Attention for Sketch ClassificationViet-Tham Huynh, Trong-Thuan Nguyen , Tam V Nguyen , and 1 more authorIn Pacific-Rim Symposium on Image and Video Technology , 2023
MobileNet-SA: Lightweight CNN with Self Attention for Sketch ClassificationViet-Tham Huynh, Trong-Thuan Nguyen , Tam V Nguyen , and 1 more authorIn Pacific-Rim Symposium on Image and Video Technology , 2023Sketch classification plays a crucial role across diverse domains, including image retrieval, artistic style analysis, and content-based image retrieval. While CNNs have demonstrated remarkable success in various image-related tasks, the computational complexity of large models poses challenges in resource-constrained environments. To address this concern, we propose MobileNet-SA, a novel lightweight model that seamlessly integrates a self-attention module into the MobileNet architecture, with a specific focus on enhancing sketch classification performance. The MobileNet-SA model leverages the inherent efficiency of lightweight CNN while harnessing the power of self-attention mechanisms to effectively capture spatial dependencies and enrich feature representations within sketch data. In our experiments, MobileNet-SA achieves state-of-the-art results, demonstrating an impressive accuracy of 93.5% on the challenging SketchyCOCO dataset and 96.7% on the GM-Sketch dataset. We thoroughly evaluate the model’s performance across diverse sketch classes, confirming its robustness and generalization capabilities, which make it well-suited for real-world applications where input sketches may exhibit significant variations. Our research indicates that MobileNet-SA not only outperforms existing methods but also offers an efficient and interpretable solution for sketch classification tasks.
@inproceedings{huynh2023mobilenet, title = {MobileNet-SA: Lightweight CNN with Self Attention for Sketch Classification}, author = {Huynh, Viet-Tham and Nguyen, Trong-Thuan and Nguyen, Tam V and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {Pacific-Rim Symposium on Image and Video Technology}, pages = {110--123}, year = {2023}, organization = {Springer}, } -
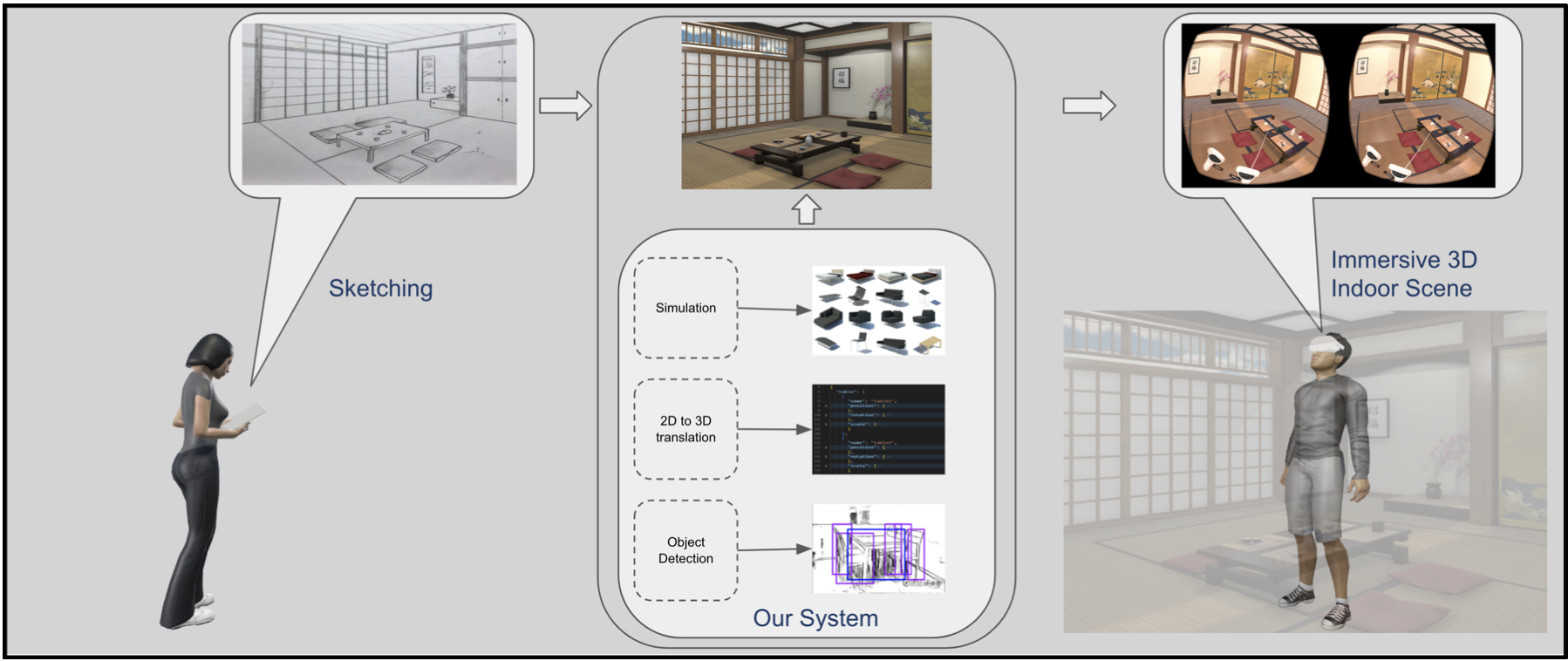 Sketch2Reality: Immersive 3D Indoor Scene Synthesis via SketchesViet-Tham Huynh, Tam V Nguyen , and Minh-Triet TranIn Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2023
Sketch2Reality: Immersive 3D Indoor Scene Synthesis via SketchesViet-Tham Huynh, Tam V Nguyen , and Minh-Triet TranIn Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2023Sketching indoor scenes is helpful in daily activities as it allows for quick visualization and planning of room layouts, furniture arrangements, design ideas, or scene creation for games and entertainment. This motivates our proposal of Sketch2Reality, a system to simplify the creation of immersive 3D indoor scenes from 2D sketch images. Users sketch their desired scene, and our system identifies sketched objects and their positions, then retrieves and populates corresponding 3D models into the generating 3D scene. Users can then modify the scene, rearrange furniture, adjust lighting, and add or remove objects. Integration with Virtual Reality technology allows users to experience and interact with the scene realistically. Our experiments with three groups of users with different experience levels in 3D scene design and creation demonstrate the efficiency and usefulness of our solution. Sketch2Reality empowers users to dynamically bring their ideas to life, combining sketching, AI assistance for 3D generation, and VR for enhanced creativity and design exploration.
@inproceedings{huynh2023sketch2reality, title = {Sketch2Reality: Immersive 3D Indoor Scene Synthesis via Sketches}, author = {Huynh, Viet-Tham and Nguyen, Tam V and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology}, pages = {863--869}, year = {2023}, } -
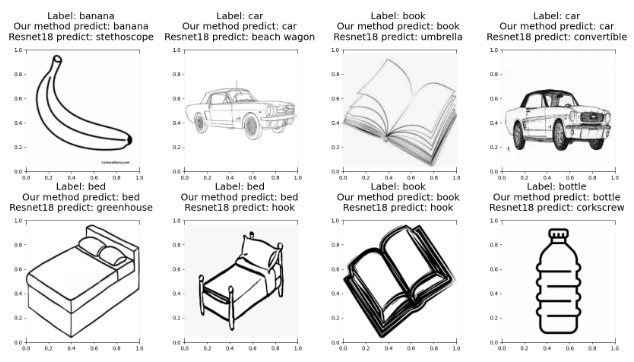 Light-weight Sketch Recognition with Knowledge DistillationViet-Tham Huynh, Tam V Nguyen , and Minh-Triet TranIn 2023 International Conference on Multimedia Analysis and Pattern Recognition (MAPR) , 2023
Light-weight Sketch Recognition with Knowledge DistillationViet-Tham Huynh, Tam V Nguyen , and Minh-Triet TranIn 2023 International Conference on Multimedia Analysis and Pattern Recognition (MAPR) , 2023Recognizing hand-drawn sketches is a promising starting point for various applications, such as assisting artists in creating 3D environments for games or virtual environment scenes quickly and efficiently from concept arts. In addition, by understanding drawings, we can generate 3D models that can be used for further design and development. Thus, in this paper, we aim to develop a novel lightweight network that can accurately recognize sketch drawings. We propose a lightweight-yet-efficient neural network based on MobileNetV2 for sketch recognition and employ knowledge distillation to train the proposed model from EfficientNet-B4. To evaluate the accuracy of the proposed method, we collect a dataset of sketches comprising 1800 drawings in 12 categories, ranging from furniture to animals. The experimental results show that our network model achieves an accuracy of 96.7%, with 96.9% precision, 96.7% recall, and 96.7% F1-score. These results demonstrate that the proposed approach has great potential for practical sketch recognition applications, such as interior design or VR scene generation.
@inproceedings{huynh2023light, title = {Light-weight Sketch Recognition with Knowledge Distillation}, author = {Huynh, Viet-Tham and Nguyen, Tam V and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {2023 International Conference on Multimedia Analysis and Pattern Recognition (MAPR)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2023}, organization = {IEEE}, } -
 Leveraging Deep Learning and Knowledge Distillation for Enhanced Traffic Anomaly Detection in Transportation SystemsMai-Khiem Tran , Viet-Tham Huynh, and Minh-Triet TranIn 2023 International Conference on Multimedia Analysis and Pattern Recognition (MAPR) , 2023
Leveraging Deep Learning and Knowledge Distillation for Enhanced Traffic Anomaly Detection in Transportation SystemsMai-Khiem Tran , Viet-Tham Huynh, and Minh-Triet TranIn 2023 International Conference on Multimedia Analysis and Pattern Recognition (MAPR) , 2023This paper introduces an innovative approach to enhance traffic anomaly detection in transportation systems using deep learning and knowledge distillation. We create a robust dataset from 427 videos containing 1,415 accident-related events, spanning various anomalies like accidents, car crashes, and pedestrian violations. To address real-time anomaly detection challenges, we propose a novel lightweight neural network architecture inspired by EfficientNet-B0, designed for efficient video anomaly detection. Through knowledge distillation, a student model learns from a teacher model’s predictions, resulting in heightened anomaly detection accuracy. Experimental results highlight the approach’s efficacy, with the knowledge-distilled student model consistently outperforming the standalone lightweight network, achieving an accuracy of 94.83% compared to 94.16%. This research offers a practical solution for real-time traffic anomaly detection, which is especially valuable in resource-constrained environments. Fusing a unique dataset, EfficientNet-B0-like structure, lightweight architecture, and knowledge distillation holds significant potential for fostering safer and more efficient transportation systems.
@inproceedings{tran2023leveraging, title = {Leveraging Deep Learning and Knowledge Distillation for Enhanced Traffic Anomaly Detection in Transportation Systems}, author = {Tran, Mai-Khiem and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {2023 International Conference on Multimedia Analysis and Pattern Recognition (MAPR)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2023}, organization = {IEEE}, } -
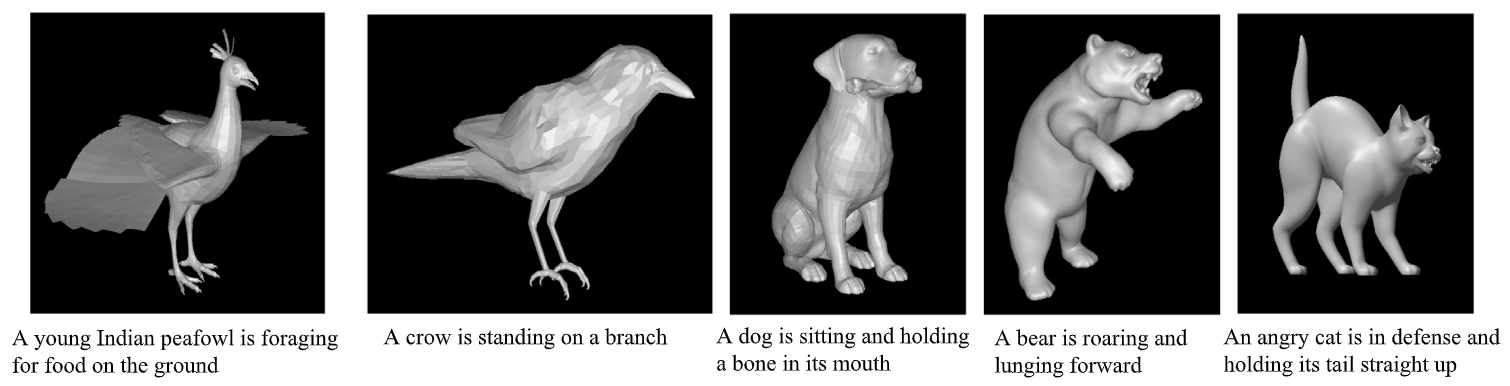 TextANIMAR: text-based 3D animal fine-grained retrievalTrung-Nghia Le , Tam V Nguyen , Minh-Quan Le , and 8 more authorsComputers & Graphics, 2023
TextANIMAR: text-based 3D animal fine-grained retrievalTrung-Nghia Le , Tam V Nguyen , Minh-Quan Le , and 8 more authorsComputers & Graphics, 20233D object retrieval is an important yet challenging task that has drawn more and more attention in recent years. While existing approaches have made strides in addressing this issue, they are often limited to restricted settings such as image and sketch queries, which are often unfriendly interactions for common users. In order to overcome these limitations, this paper presents a novel SHREC challenge track focusing on text-based fine-grained retrieval of 3D animal models. Unlike previous SHREC challenge tracks, the proposed task is considerably more challenging, requiring participants to develop innovative approaches to tackle the problem of text-based retrieval. Despite the increased difficulty, we believe this task can potentially drive useful applications in practice and facilitate more intuitive interactions with 3D objects. Five groups participated in our competition, submitting a total of 114 runs. While the results obtained in our competition are satisfactory, we note that the challenges presented by this task are far from fully solved. As such, we provide insights into potential areas for future research and improvements. We believe we can help push the boundaries of 3D object retrieval and facilitate more user-friendly interactions via vision-language technologies.
@article{le2023textanimar, title = {TextANIMAR: text-based 3D animal fine-grained retrieval}, author = {Le, Trung-Nghia and Nguyen, Tam V and Le, Minh-Quan and Nguyen, Trong-Thuan and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Do, Trong-Le and Le, Khanh-Duy and Tran, Mai-Khiem and Hoang-Xuan, Nhat and Nguyen-Ho, Thang-Long and others}, journal = {Computers \& Graphics}, volume = {116}, pages = {162--172}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Elsevier}, } -
 News event retrieval from large video collection in Ho Chi Minh City AI challenge 2023Trong-Le Do , Hai-Dang Nguyen , Quang-Thuc Nguyen , and 8 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2023
News event retrieval from large video collection in Ho Chi Minh City AI challenge 2023Trong-Le Do , Hai-Dang Nguyen , Quang-Thuc Nguyen , and 8 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology , 2023Event retrieval from large collections of TV news videos is crucial for efficient information access, enabling researchers, journalists, and the general public to quickly locate and analyze relevant content amidst the vast sea of news coverage, facilitating informed decision-making and a comprehensive understanding of significant events. This paper presents an overview of the AI-driven video retrieval task in Ho Chi Minh City AI Challenge 2023. The competition draws inspiration from internationally recognized competitions, namely the Video Browser Showdown (VBS) and the Lifelog Search Challenge (LSC). Participants are tasked with developing AI models to retrieve specific video segments from a diverse dataset from reputable news channels. The dataset comprises a vast collection of videos, keyframes, object detections, CLIP features, and metadata. It is divided into three packs with a total of 1,270 videos, spanning approximately 360 hours of content. The challenge comprises two groups. Group A is open to students, researchers, and practitioners in artificial intelligence and information retrieval, emphasizing substantial knowledge and experience. Group B is tailored for high school students, focusing on nurturing interest, learning, and engagement among the next generation of AI enthusiasts. The wide variation in the content of queries challenged participants to demonstrate their adaptability and creativity in effectively retrieving diverse events from the extensive TV news video dataset. The winning teams showcased promising solutions by effectively harnessing artificial intelligence and information retrieval techniques to excel in event retrieval from a vast collection of TV news videos.
@inproceedings{do2023news, title = {News event retrieval from large video collection in Ho Chi Minh City AI challenge 2023}, author = {Do, Trong-Le and Nguyen, Hai-Dang and Nguyen, Quang-Thuc and Tran, Mai-Khiem and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Gurrin, Cathal and Ninh, Tu V and Le, Tu-Khiem and Ngo, Thanh Duc and Ngo, Tu-Trinh and others}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology}, pages = {1011--1017}, year = {2023}, } -
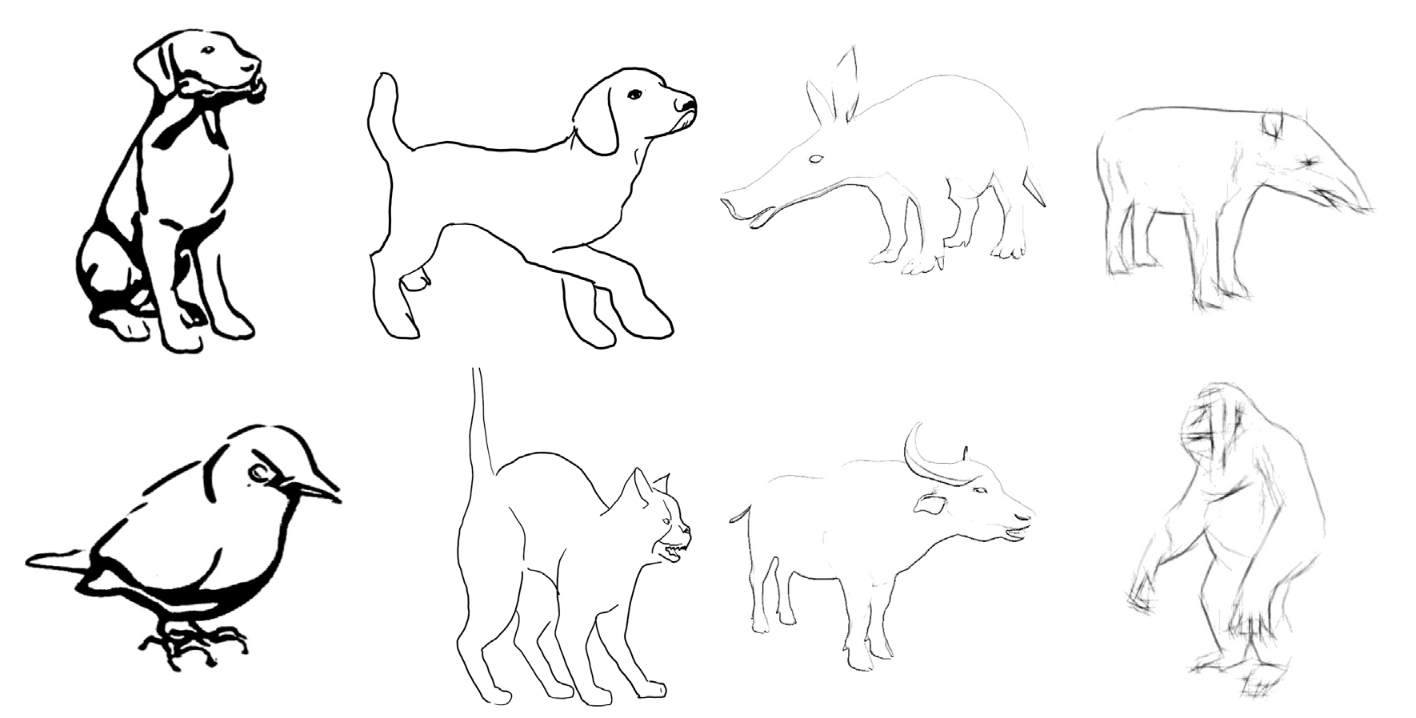 SketchANIMAR: sketch-based 3D animal fine-grained retrievalTrung-Nghia Le , Tam V Nguyen , Minh-Quan Le , and 8 more authorsComputers & Graphics, 2023
SketchANIMAR: sketch-based 3D animal fine-grained retrievalTrung-Nghia Le , Tam V Nguyen , Minh-Quan Le , and 8 more authorsComputers & Graphics, 2023The retrieval of 3D objects has gained significant importance in recent years due to its broad range of applications in computer vision, computer graphics, virtual reality, and augmented reality. However, the retrieval of 3D objects presents significant challenges due to the intricate nature of 3D models, which can vary in shape, size, and texture, and have numerous polygons and vertices. To this end, we introduce a novel SHREC challenge track that focuses on retrieving relevant 3D animal models from a dataset using sketch queries and expedites accessing 3D models through available sketches. Furthermore, a new dataset named ANIMAR was constructed in this study, comprising a collection of 711 unique 3D animal models and 140 corresponding sketch queries. Our contest requires participants to retrieve 3D models based on complex and detailed sketches. We receive satisfactory results from eight teams and 204 runs. Although further improvement is necessary, the proposed task has the potential to incentivize additional research in the domain of 3D object retrieval, potentially yielding benefits for a wide range of applications. We also provide insights into potential areas of future research, such as improving techniques for feature extraction and matching and creating more diverse datasets to evaluate retrieval performance.
@article{le2023sketchanimar, title = {SketchANIMAR: sketch-based 3D animal fine-grained retrieval}, author = {Le, Trung-Nghia and Nguyen, Tam V and Le, Minh-Quan and Nguyen, Trong-Thuan and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Do, Trong-Le and Le, Khanh-Duy and Tran, Mai-Khiem and Hoang-Xuan, Nhat and Nguyen-Ho, Thang-Long and others}, journal = {Computers \& Graphics}, volume = {116}, pages = {150--161}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Elsevier}, }
2022
-
 Chemisim: A Web-based VR Simulator for Chemistry ExperimentsHoang-Minh Le , Gia-Huy Nguyen , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 4 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) , 2022
Chemisim: A Web-based VR Simulator for Chemistry ExperimentsHoang-Minh Le , Gia-Huy Nguyen , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 4 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) , 2022In developing countries, high schoolers rarely have opportunities to conduct chemical experiments due to the lack of facilities. There-fore, chemistry experiment simulation is an alternative environment for students to do the chemistry lab assignments. Despite the need of creating virtual simulations to expand the application usability, it is challenging to synthesize a realistic environment given the limited computing resources. In this paper, we propose Chemisim, a highly realistic web-based VR laboratory simulation for students with high quality and usability. In particular, we make use of the fluid simulation system to mimic real chemical reactions. The imple-mented simulation was based on the chemistry assignments in the national education system, consulted by chemical teachers. Then we deployed the simulator on the web to promote a wide range of students usage. The system was evaluated by collecting and analyzing feedback from chemical teachers based on four criteria, namely, convenience, realism, functionality, and preferences. Our experimental findings address educational challenges and produce innovative technical solutions to solve them in developing countries.
@inproceedings{le2022chemisim, title = {Chemisim: A Web-based VR Simulator for Chemistry Experiments}, author = {Le, Hoang-Minh and Nguyen, Gia-Huy and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Le, Minh-Kha and Tran, Minh-Triet and Nguyen, Tam V and Tran, Thanh Ngoc-Dat}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct)}, pages = {850--854}, year = {2022}, organization = {IEEE}, } -
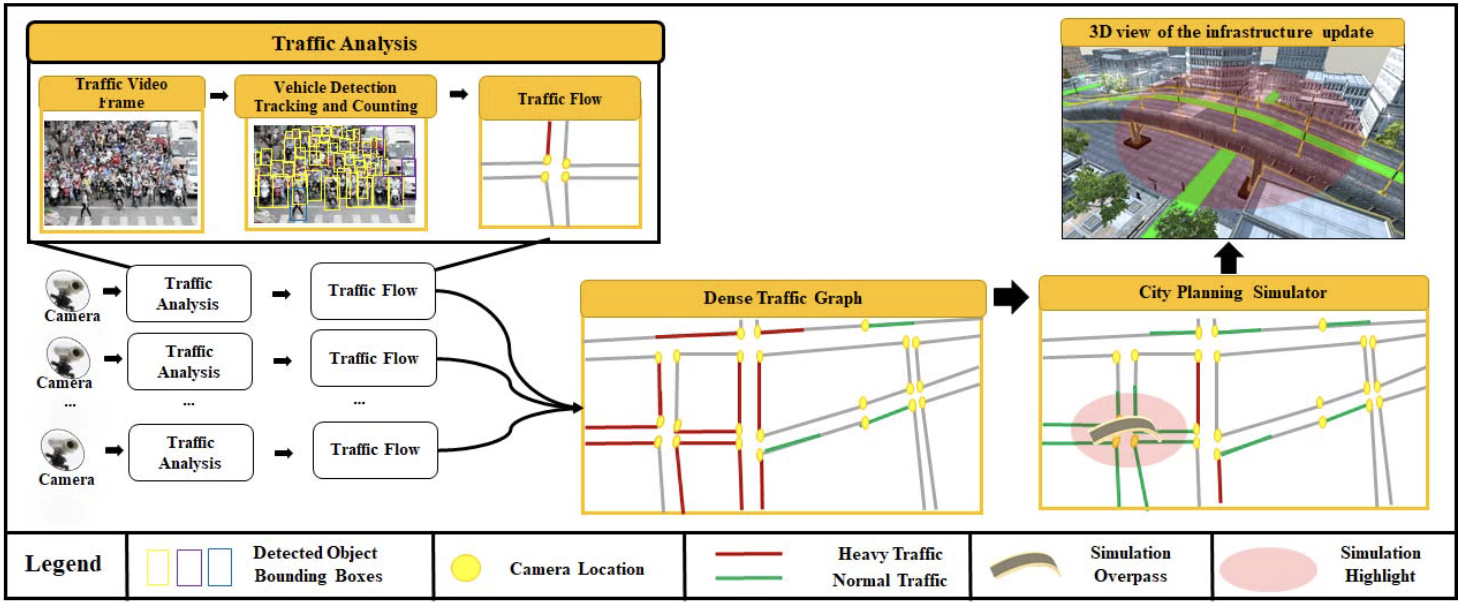 Data-Driven City Traffic Planning SimulationTam V Nguyen , Thanh Ngoc-Dat Tran , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 6 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) , 2022
Data-Driven City Traffic Planning SimulationTam V Nguyen , Thanh Ngoc-Dat Tran , Viet-Tham Huynh, and 6 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) , 2022Big cities are well-known for their traffic congestion and high density of vehicles such as cars, buses, trucks, and even a swarm of motorbikes that overwhelm city streets. Large-scale development projects have exacerbated urban conditions, making traffic congestion more severe. In this paper, we proposed a data-driven city traffic planning simulator. In particular, we make use of the city camera system for traffic analysis. It seeks to recognize the traffic vehicles and traffic flows, with reduced intervention from monitoring staff. Then, we develop a city traffic planning simulator upon the analyzed traffic data. The simulator is used to support metropolitan transportation planning. Our experimental findings address traffic planning challenges and the innovative technical solutions needed to solve them in big cities.
@inproceedings{nguyen2022data, title = {Data-Driven City Traffic Planning Simulation}, author = {Nguyen, Tam V and Tran, Thanh Ngoc-Dat and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Truong, Bao and Le, Minh-Quan and Kumavat, Mohit and Patel, Vatsa S and Tran, Mai-Khiem and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct)}, pages = {859--864}, year = {2022}, organization = {IEEE}, } -
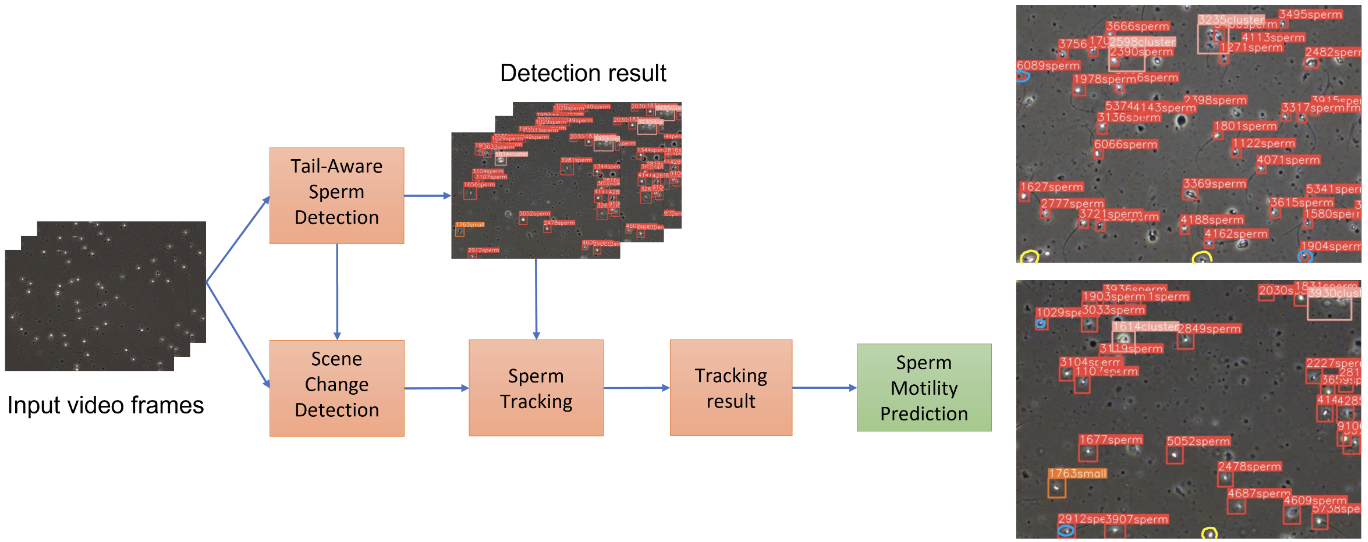 Tail-Aware Sperm Analysis for Transparent Tracking of SpermatozoaTuan-Luc Huynh , Huu-Hung Nguyen , Xuan-Nhat Hoang , and 6 more authorsIn MediaEval 2022 Workshop , 2022
Tail-Aware Sperm Analysis for Transparent Tracking of SpermatozoaTuan-Luc Huynh , Huu-Hung Nguyen , Xuan-Nhat Hoang , and 6 more authorsIn MediaEval 2022 Workshop , 2022Semen analysis is crucial to determine men’s fertility; however, microscope-based manual spermatozoa evaluation is time-consuming and costly. Therefore, it has become essential to develop computeraided-semen-analysis systems. To facilitate automated spermatozoa analysis, we propose a simple yet efficient framework for tracking sperms and predicting their motility. Different from existing methods, our proposed framework centralizes a new paradigm, dubbed sperm having a tail. We develop a novel tail-aware sperm detection model to advance the detection ability of dense, tiny, and transparent sperm cells. Furthermore, to enhance sperm tracking, a scene change detection technique is utilized to suppress identity assignment errors of similar sperms, resulting in improved sperm motility measurement. Experimental results show that our framework works well with an insignificant trade-off in execution time, which is suitable for the real-time clinical setting requirement.
@inproceedings{huynh2022tail, title = {Tail-Aware Sperm Analysis for Transparent Tracking of Spermatozoa}, author = {Huynh, Tuan-Luc and Nguyen, Huu-Hung and Hoang, Xuan-Nhat and Dao, Thao Thi Phuong and Nguyen, Tien-Phat and Huynh, Viet-Tham and Nguyen, Hai-Dang and Le, Trung-Nghia and Tran, Minh-Triet}, booktitle = {MediaEval 2022 Workshop}, year = {2022}, }